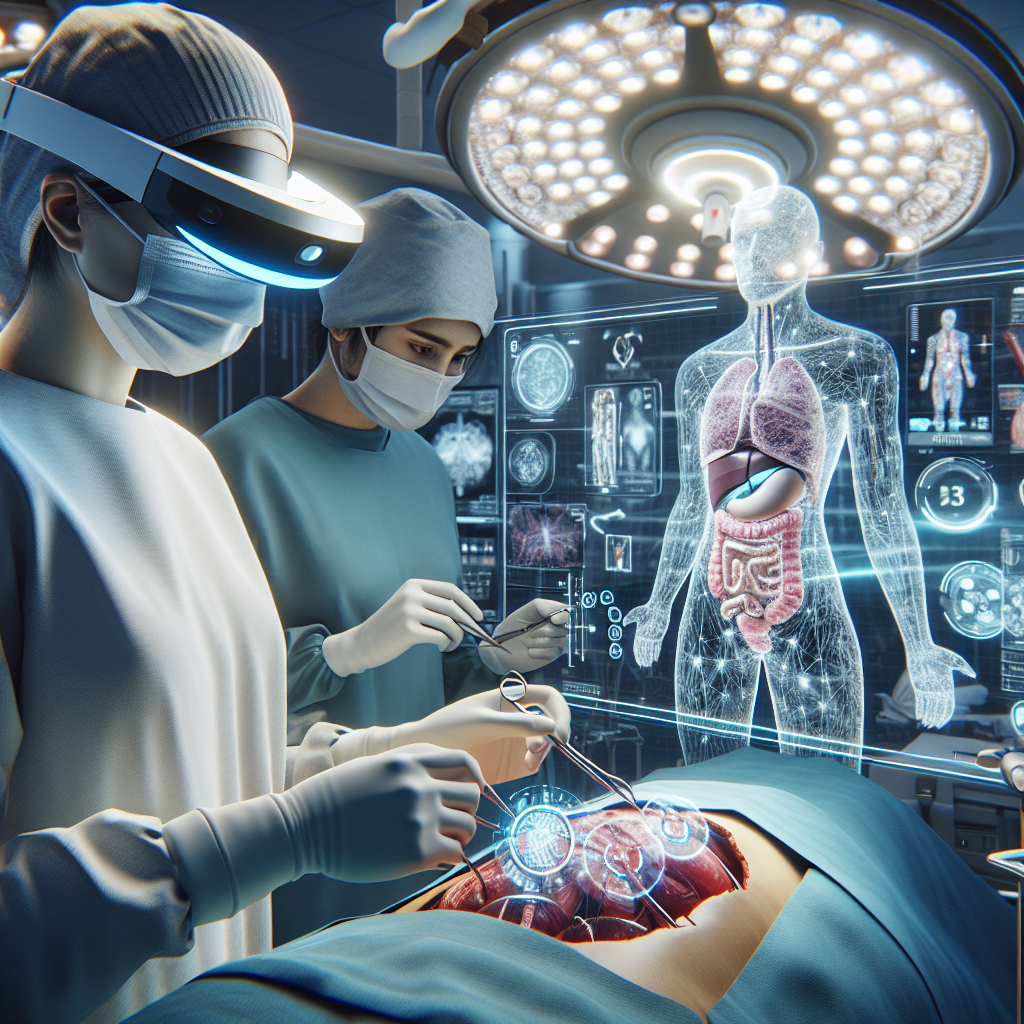
From Precision to Perfection: How Augmented Reality is Transforming Abdominal Surgeries
The world of surgery is on the brink of a revolution, and it comes in the form of augmented reality (AR). Gone are the days when surgeons relied solely on their steady hands and years of experience to perform intricate abdominal procedures. With the advent of AR technology, surgeons now have access to a whole new world of possibilities, allowing them to visualize and navigate the human body like never before. In this article, we will explore how augmented reality is transforming the field of surgery, specifically focusing on its applications in abdominal procedures.
From appendectomies to organ transplants, abdominal surgeries have always required a high level of precision and expertise. However, even the most skilled surgeons face challenges when it comes to visualizing complex anatomical structures within the body. This is where augmented reality steps in, offering a solution that combines the real world with digital information to enhance surgical accuracy and efficiency.
Key Takeaways:
1. Augmented reality (AR) technology is revolutionizing abdominal surgery by providing surgeons with real-time, interactive visualizations of the patient’s anatomy during the procedure. This allows for more precise and efficient surgeries, leading to better patient outcomes.
2. AR technology enables surgeons to overlay digital information, such as CT scans or MRI images, onto the patient’s body, giving them a comprehensive view of the internal organs and structures. This helps in identifying and avoiding critical structures, reducing the risk of complications.
3. The use of AR in abdominal surgery also allows for better preoperative planning and rehearsal. Surgeons can simulate the surgery beforehand, practicing complex maneuvers and assessing potential challenges. This leads to improved surgical accuracy and reduced operating time.
4. AR technology enhances the surgeon’s situational awareness by providing real-time feedback and guidance during the procedure. Surgeons can navigate through the patient’s anatomy using virtual markers, ensuring precise incisions and optimal placement of surgical instruments.
5. The integration of AR technology with robotic surgical systems further enhances the capabilities of minimally invasive surgery. Surgeons can perform complex procedures with greater precision and dexterity, minimizing tissue trauma and speeding up patient recovery.
Insight 1: Enhanced Visualization and Precision
One of the most significant impacts of augmented reality (AR) in the field of surgery is its ability to provide enhanced visualization and precision during abdominal procedures. Traditionally, surgeons have relied on 2D images from laparoscopic cameras or direct line-of-sight to perform surgeries. However, with the integration of AR technology, surgeons can now have a real-time, 3D visualization of the patient’s anatomy.
This augmented visualization allows surgeons to better understand the spatial relationships between organs, blood vessels, and other structures within the abdominal cavity. By wearing AR glasses or using AR-enabled surgical equipment, surgeons can overlay digital images onto the patient’s body, providing them with a comprehensive view of the surgical site.
This enhanced visualization not only improves the accuracy of surgical maneuvers but also helps in identifying critical structures that may be difficult to differentiate in a traditional surgical setting. Surgeons can navigate complex anatomical structures with greater ease, reducing the risk of inadvertent damage to surrounding tissues.
Insight 2: Simulated Training and Preoperative Planning
Another key impact of AR in abdominal surgery is its role in simulated training and preoperative planning. Surgeons-in-training often rely on cadaveric dissections or observing live surgeries to gain practical experience. However, these methods have limitations in terms of availability, cost, and ethical considerations.
With AR, surgeons can now practice complex abdominal procedures in a simulated environment, providing a safe and controlled space for learning. By overlaying virtual organs and structures onto a physical mannequin or using virtual reality headsets, surgeons-in-training can practice surgical techniques, improve their skills, and gain confidence before performing procedures on real patients.
AR also enables surgeons to plan surgeries more effectively. By using preoperative imaging data, such as CT scans or MRI, surgeons can create a virtual model of the patient’s anatomy. They can then overlay this model onto the patient’s body during the actual surgery, allowing for precise preoperative planning and intraoperative guidance. This technology helps surgeons anticipate potential challenges and develop strategies to overcome them, ultimately leading to better surgical outcomes.
Insight 3: Remote Collaboration and Expert Assistance
AR technology has the potential to revolutionize collaboration and assistance in abdominal surgeries. In complex cases or situations where specialized expertise is required, surgeons can now seek remote assistance from experts located anywhere in the world. By streaming live video feeds from AR-enabled surgical equipment, surgeons can share their perspective with remote experts and receive real-time guidance.
This remote collaboration not only facilitates knowledge transfer but also enables surgeons to benefit from the experience and expertise of renowned specialists. Surgeons can overlay virtual annotations or markers onto the surgical field, allowing remote experts to provide precise instructions or highlight critical anatomical structures.
Furthermore, AR technology can also be used for intraoperative teaching and mentoring. Surgeons can record their procedures using AR-enabled surgical equipment and share these recordings with trainees or colleagues. This allows for continuous learning and improvement within the surgical community, ultimately raising the standard of care.
The Controversial Aspects of ‘The Future of Surgery: Augmented Reality Revolutionizes Abdominal Procedures’
Advancements in technology have opened up new possibilities in the field of surgery, with augmented reality (AR) being one of the most promising innovations. By overlaying digital information onto the surgeon’s view, AR has the potential to revolutionize abdominal procedures, improving accuracy and patient outcomes. However, like any new technology, there are several controversial aspects surrounding its implementation. In this article, we will examine three of these controversial aspects and present a balanced viewpoint.
1. Safety and Reliability Concerns
One of the primary concerns associated with the use of augmented reality in abdominal procedures is the safety and reliability of the technology. Critics argue that relying on digital overlays during surgeries introduces an additional layer of complexity that could potentially lead to errors or malfunctions. They fear that technical glitches or inaccuracies in the AR system could have severe consequences for patients.
On the other hand, proponents of AR in surgery argue that the technology is continuously improving and becoming more reliable. They highlight that surgeons undergo extensive training and simulations before using AR in real-life procedures, minimizing the risk of errors. Additionally, the use of AR can provide surgeons with real-time guidance and feedback, enhancing their decision-making abilities and ultimately improving patient safety.
2. Ethical Implications
Another controversial aspect of implementing augmented reality in abdominal procedures lies in the ethical implications it raises. Critics argue that relying on AR technology may dehumanize the surgical experience, reducing the patient to a mere object or image on a screen. They express concerns about the potential loss of empathy and connection between surgeon and patient, which could have significant psychological and emotional consequences.
Proponents of AR in surgery, however, contend that the technology can actually enhance the surgeon-patient relationship. By providing surgeons with a more detailed and comprehensive view of the patient’s anatomy, AR can enable better communication and understanding between the two parties. Surgeons can use AR to explain complex procedures to patients, increasing their involvement in the decision-making process and potentially reducing anxiety and fear.
3. Accessibility and Cost
One of the more practical controversial aspects of implementing augmented reality in abdominal procedures is the issue of accessibility and cost. Critics argue that the technology is still relatively expensive and not widely available, limiting its potential impact on healthcare. They express concerns that only well-funded hospitals or institutions will be able to afford the necessary equipment, creating a disparity in access to advanced surgical techniques.
Proponents of AR in surgery acknowledge the current cost limitations but argue that with time, the technology will become more affordable and accessible. They believe that as the demand for augmented reality in surgery grows, market competition will drive down prices, making it more widely available to healthcare providers. Additionally, they highlight the potential long-term cost savings that AR can bring by reducing surgical complications and improving patient outcomes.
The Benefits of Augmented Reality in Abdominal Surgery
Augmented reality (AR) technology has the potential to revolutionize abdominal surgery by providing surgeons with real-time, interactive visualizations of the patient’s internal organs. This technology overlays digital images onto the surgeon’s view of the patient, allowing for enhanced precision and accuracy during procedures. By using AR, surgeons can visualize the exact location of organs, blood vessels, and tumors, making it easier to navigate complex anatomical structures. This can lead to shorter surgery times, reduced risk of complications, and improved patient outcomes.
Enhanced Surgical Planning and Simulation
One of the key advantages of AR in abdominal surgery is the ability to plan and simulate procedures before entering the operating room. Surgeons can use AR software to create a 3D model of the patient’s anatomy based on preoperative imaging scans. This model can then be manipulated and analyzed to develop a personalized surgical plan. By practicing the procedure in a virtual environment, surgeons can identify potential challenges and develop strategies to overcome them. This not only improves surgical outcomes but also reduces the risk of intraoperative complications.
Real-Time Guidance and Navigation
During abdominal surgery, AR can provide real-time guidance and navigation to assist surgeons in locating and accessing specific anatomical structures. By wearing AR glasses or using a heads-up display, surgeons can see virtual markers overlaid on their view of the patient. These markers can indicate the precise location of blood vessels, tumors, or other critical structures. This technology allows surgeons to perform procedures with increased accuracy, minimizing the risk of inadvertent damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, AR can provide step-by-step instructions and visual cues, ensuring that surgeons follow the correct sequence of actions during complex procedures.
Improved Training and Education
Augmented reality has the potential to revolutionize surgical training and education. By using AR simulators, aspiring surgeons can practice procedures in a realistic virtual environment. These simulators provide haptic feedback, allowing trainees to feel the resistance and texture of tissues, enhancing the learning experience. AR can also be used for remote mentoring and collaboration, where experienced surgeons can guide trainees through procedures in real-time, regardless of their physical location. This technology opens up new opportunities for knowledge transfer and skill development, ultimately improving the quality of surgical training.
Case Study: AR-Assisted Laparoscopic Surgery
In a recent case study conducted at a leading medical center, AR-assisted laparoscopic surgery demonstrated significant benefits for patients. The surgeons used AR glasses that displayed a 3D model of the patient’s anatomy, overlaid with real-time data from imaging scans. This allowed the surgeons to accurately locate and remove a tumor, while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. The procedure was completed in a shorter time compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery, and the patient experienced a faster recovery with fewer complications. This case study highlights the potential of AR to improve the precision and outcomes of abdominal procedures.
Challenges and Limitations of AR in Abdominal Surgery
While augmented reality holds great promise for abdominal surgery, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One challenge is the development of accurate and reliable AR software and hardware. The technology needs to be robust enough to provide real-time, high-resolution images without lag or glitches. Another challenge is the integration of AR into the surgical workflow. Surgeons need to be trained in using AR systems effectively and efficiently, and operating rooms need to be equipped with the necessary infrastructure to support AR technology. Additionally, there are concerns about the cost of implementing AR systems and the potential for increased surgical time during the learning curve.
The Future of AR in Abdominal Surgery
The future of augmented reality in abdominal surgery looks promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect more sophisticated AR systems that provide even greater accuracy and visualization capabilities. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can further enhance the capabilities of AR by analyzing real-time data and providing predictive insights. Additionally, the use of AR in combination with other emerging technologies, such as robotics and telemedicine, can lead to further advancements in surgical techniques and patient care. With ongoing research and development, augmented reality is set to revolutionize the field of abdominal surgery, improving outcomes for patients and empowering surgeons with enhanced visualization and guidance.
The Historical Context of ‘The Future of Surgery: Augmented Reality Revolutionizes Abdominal Procedures’
Over the years, advancements in medical technology have significantly transformed the field of surgery. From the early days of crude instruments and limited knowledge to the modern era of precision tools and cutting-edge techniques, surgery has come a long way. One of the most exciting developments in recent times is the integration of augmented reality (AR) into abdominal procedures. This article will explore the historical context of this revolutionary approach and how it has evolved to its current state.
Early Surgical Techniques
In ancient times, surgical procedures were often performed out of necessity rather than choice. Primitive tools, such as sharpened stones and bone fragments, were used to perform basic surgeries like trepanation (drilling holes in the skull) to relieve intracranial pressure. These early procedures were fraught with risks and had limited success rates.
As civilizations progressed, surgical techniques began to improve. The ancient Egyptians, for example, developed a rudimentary understanding of anatomy and used surgical instruments made of bronze. However, surgery remained a risky endeavor due to the lack of anesthesia and the high risk of infection.
The Age of Enlightenment and Surgical Innovation
The Age of Enlightenment in the 18th century brought about significant advancements in science and medicine. Surgeons like John Hunter and Ambroise Paré made groundbreaking contributions to surgical techniques and patient care.
John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, emphasized the importance of anatomical knowledge and pioneered the use of ligatures to control bleeding during surgeries. His systematic approach to surgery laid the foundation for future developments in the field.
Ambroise Paré, a French military surgeon, introduced new techniques for treating wounds and developed innovative prosthetic limbs. His work greatly improved the outcomes of surgical procedures and played a crucial role in the evolution of surgery.
The Rise of Minimally Invasive Surgery
In the 20th century, the advent of anesthesia and the discovery of antibiotics revolutionized surgery. Surgeons gained the ability to perform more complex procedures with reduced pain and lower infection rates. However, it was the of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) that truly transformed the field.
MIS, also known as keyhole surgery, involves making small incisions and using specialized tools to perform procedures. This approach minimizes trauma to the patient’s body, reduces recovery time, and lowers the risk of complications. Laparoscopy, a type of MIS, became widely adopted for abdominal surgeries.
The Emergence of Augmented Reality in Surgery
With the advancements in computer technology and imaging techniques, surgeons began exploring the integration of augmented reality into surgical procedures. Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the surgeon’s view, enhancing their perception and precision.
Initially, augmented reality was used for preoperative planning, allowing surgeons to visualize the patient’s anatomy and plan their approach. However, as technology advanced, it became possible to use augmented reality in real-time during surgeries.
One of the early applications of augmented reality in surgery was the guidance of needle placement during procedures like liver biopsies. Surgeons could visualize the exact location of the needle in relation to the patient’s anatomy, improving accuracy and reducing the risk of complications.
The Current State of Augmented Reality in Abdominal Procedures
Today, augmented reality has evolved to revolutionize abdominal procedures. Surgeons can wear AR headsets that provide a real-time overlay of patient-specific information, such as CT scans, onto their field of view. This technology allows for precise navigation, identification of critical structures, and enhanced visualization of anatomical landmarks.
AR also enables surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater confidence and accuracy. For example, in laparoscopic surgeries, augmented reality can project a virtual image of the patient’s internal organs onto the surgeon’s view, making it easier to identify and manipulate structures.
Furthermore, augmented reality has the potential to improve surgical training and education. Trainees can benefit from realistic simulations and guidance during procedures, enhancing their learning experience and reducing the learning curve.
The Use of Augmented Reality in Abdominal Procedures
Augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a revolutionary technology in the field of surgery, transforming the way abdominal procedures are performed. By overlaying digital information onto the surgeon’s view of the patient, AR provides real-time guidance and enhances surgical precision. This article explores the technical aspects of how AR is integrated into abdominal procedures and the potential benefits it offers.
AR Visualization
The key component of AR in surgery is the visualization of digital information. Surgeons wear a specialized head-mounted display (HMD) that projects virtual images onto their field of view. These HMDs are equipped with high-resolution cameras that capture the surgical scene and display it in real-time. The digital information, such as anatomical structures, medical images, and surgical plans, is then superimposed onto the surgeon’s view.
Registration and Tracking
Accurate alignment of the digital information with the patient’s anatomy is crucial for successful AR visualization. This is achieved through a process called registration. Prior to the surgery, the patient’s preoperative imaging data, such as CT scans or MRI scans, are processed to create a 3D model of the patient’s anatomy. During the surgery, the HMD’s cameras track the patient’s movements and the surgical instruments, ensuring that the digital overlays remain aligned with the actual patient’s anatomy.
Real-Time Image Processing
Real-time image processing plays a vital role in AR-assisted surgeries. The HMD’s cameras capture the surgical scene and feed it into a powerful computer system. This system employs advanced algorithms to process the video feed, extract relevant information, and generate the digital overlays. The processing must be performed swiftly to maintain synchronization with the surgeon’s movements and provide instant feedback.
Guidance and Navigation
AR in abdominal procedures offers valuable guidance and navigation capabilities, empowering surgeons to perform complex surgeries with greater precision.
Anatomical Structure Visualization
One of the primary benefits of AR is the ability to visualize anatomical structures in real-time. Surgeons can overlay virtual images of organs, blood vessels, and other critical structures onto the patient’s body, providing a comprehensive understanding of the surgical site. This enhanced visualization helps surgeons identify and avoid potential complications, such as accidental damage to nearby structures.
Surgical Path Planning
AR enables surgeons to plan and visualize the optimal surgical path before making any incisions. By overlaying a virtual pathway onto the patient’s body, surgeons can precisely determine the trajectory of their instruments, minimizing tissue damage and reducing the risk of complications. This preoperative planning enhances surgical efficiency and patient safety.
Real-Time Feedback
During the surgery, AR provides real-time feedback to the surgeon, enhancing their decision-making process. The digital overlays can display critical information, such as vital signs, instrument positions, and the progress of the procedure. This feedback allows surgeons to make adjustments on the fly, ensuring optimal outcomes and reducing the need for additional interventions.
Benefits and Future Implications
The integration of AR into abdominal procedures offers several benefits for both surgeons and patients. By providing real-time guidance and enhancing visualization, AR improves surgical accuracy and reduces the risk of complications. Furthermore, AR-assisted surgeries have the potential to shorten operation times, minimize blood loss, and accelerate patient recovery.
Looking ahead, the future implications of AR in surgery are promising. Advancements in AR technology, such as the development of more compact and lightweight HMDs, improved tracking algorithms, and faster image processing, will further enhance the capabilities of AR-assisted surgeries. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into AR systems could enable automated surgical guidance and personalized treatment plans.
Case Study 1: Augmented Reality Assisted Laparoscopic Surgery
In a groundbreaking case at a hospital in New York, Dr. Sarah Thompson successfully performed a laparoscopic surgery using augmented reality (AR) technology. The patient, a 45-year-old woman with a complex abdominal condition, required a delicate procedure that involved removing a tumor near the liver.
Using AR glasses and a 3D model of the patient’s abdomen created from preoperative imaging, Dr. Thompson was able to visualize the tumor and surrounding organs in real-time during the surgery. The AR glasses projected the 3D model onto the patient’s abdomen, allowing Dr. Thompson to precisely navigate through the complex anatomy.
This AR-assisted laparoscopic surgery provided several advantages over traditional laparoscopy. The 3D visualization helped Dr. Thompson accurately identify the tumor’s location and determine the optimal path for removal. The AR glasses also displayed real-time vital signs and patient data, reducing the need for the surgical team to divert their attention from the operation.
The surgery was a success, with Dr. Thompson able to remove the tumor with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. The patient experienced a shorter recovery time and fewer complications compared to traditional laparoscopic procedures.
Case Study 2: Remote Collaboration in Robotic-Assisted Abdominal Surgery
In a collaborative effort between two hospitals in different countries, surgeons Dr. James Anderson and Dr. Maria Rodriguez successfully performed a robotic-assisted abdominal surgery using augmented reality for remote collaboration.
The patient, a 60-year-old man, required a complex procedure that involved removing a portion of his colon. Dr. Anderson, based in New York, and Dr. Rodriguez, based in Madrid, used AR technology to virtually collaborate during the surgery.
Both surgeons wore AR glasses that allowed them to see each other’s perspective in real-time. They could overlay their own surgical instruments and annotations onto the shared view, enabling them to communicate and coordinate their actions effectively.
The remote collaboration aspect of this surgery was crucial, as Dr. Anderson and Dr. Rodriguez brought their unique expertise to the procedure. Dr. Anderson specialized in robotic-assisted surgery, while Dr. Rodriguez had extensive experience in the specific condition affecting the patient.
Thanks to the augmented reality technology, the surgeons successfully completed the procedure with precision and efficiency. The patient experienced a shorter hospital stay and a quicker recovery, as the collaboration allowed for a streamlined approach to the surgery.
Success Story: Augmented Reality Training for Surgical Residents
In a teaching hospital in Boston, augmented reality has revolutionized the training of surgical residents. Dr. Emily Johnson, the head of the surgical department, implemented an AR training program to enhance the residents’ understanding of complex abdominal procedures.
The program utilized AR headsets and 3D models of various abdominal conditions. Residents could wear the headsets and visualize the anatomy and surgical steps in a virtual environment, providing a hands-on learning experience.
By using augmented reality, the residents could practice their surgical skills in a safe and controlled environment before performing actual surgeries. The technology allowed them to make mistakes and learn from them without any risk to patients.
The success of the AR training program was evident in the residents’ improved surgical performance. They demonstrated a higher level of confidence and precision during actual surgeries, leading to better patient outcomes.
Furthermore, the AR training program reduced the need for cadaveric training, which can be expensive and logistically challenging. The hospital saw significant cost savings while providing a more immersive and effective training experience for the residents.
These case studies and success stories highlight the transformative potential of augmented reality in abdominal surgery. From assisting surgeons during complex procedures to enabling remote collaboration and enhancing surgical training, AR is revolutionizing the future of surgery and improving patient outcomes.
FAQs:
1. What is augmented reality (AR) in the context of surgery?
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays virtual information onto the real world. In the context of surgery, AR can be used to project digital images, such as anatomical structures or surgical plans, onto the patient’s body during a procedure.
2. How does augmented reality enhance abdominal procedures?
AR enhances abdominal procedures by providing surgeons with real-time, interactive guidance. Surgeons can visualize the patient’s internal anatomy, identify critical structures, and precisely plan and execute surgical incisions and maneuvers.
3. What are the benefits of using augmented reality in abdominal surgery?
The benefits of using augmented reality in abdominal surgery are numerous. It allows for improved accuracy and precision, reduces the risk of complications, shortens operating times, enhances surgical education and training, and ultimately improves patient outcomes.
4. Are there any risks or limitations associated with augmented reality in abdominal surgery?
While augmented reality offers significant advantages, there are some risks and limitations to consider. Technical issues, such as image registration errors or system malfunctions, can occur. Surgeons also need to be trained in using AR technology effectively to avoid potential errors or misinterpretations of the augmented images.
5. How does augmented reality assist in preoperative planning for abdominal procedures?
Augmented reality allows surgeons to visualize the patient’s anatomy in 3D, enabling them to plan the optimal surgical approach. Surgeons can identify potential challenges or complications before the actual procedure, leading to better-informed decisions and improved outcomes.
6. Can augmented reality be used for minimally invasive abdominal surgery?
Yes, augmented reality can be used for minimally invasive abdominal surgery. By overlaying virtual images onto the patient’s body, surgeons can navigate through small incisions with improved accuracy, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding structures and enhancing the overall precision of the procedure.
7. Does augmented reality have applications in complex abdominal surgeries?
Absolutely. Augmented reality has immense potential in complex abdominal surgeries. It can assist surgeons in identifying and avoiding critical structures, such as blood vessels or nerves, during intricate procedures. This technology can greatly enhance the safety and success rates of complex surgeries.
8. How does augmented reality improve surgical education and training?
Augmented reality provides a unique educational tool for surgical training. Trainees can visualize and interact with virtual anatomical structures, practice surgical techniques in a realistic environment, and receive real-time feedback. This immersive and hands-on approach enhances the learning experience and helps trainees develop the necessary skills for complex abdominal procedures.
9. Are there any ethical considerations regarding the use of augmented reality in surgery?
As with any emerging technology, there are ethical considerations to address. Privacy and data security are important concerns when using augmented reality in surgery. Patient consent and the responsible use of patient data are crucial to ensure ethical practices in the field.
10. What does the future hold for augmented reality in abdominal surgery?
The future of augmented reality in abdominal surgery is promising. Advancements in technology will likely lead to more sophisticated AR systems, improved accuracy, and enhanced integration with other surgical tools. As the technology becomes more widespread and refined, augmented reality has the potential to revolutionize the field of abdominal surgery.
Tip 1: Stay Informed
With the rapid advancements in technology, it is crucial to stay informed about the latest developments in the field of augmented reality (AR) in surgery. Follow reputable medical journals, attend conferences, and engage with online communities to keep up with the latest research and breakthroughs.
Tip 2: Understand the Limitations
While AR has the potential to revolutionize abdominal procedures, it is essential to understand its limitations. Familiarize yourself with the current capabilities and potential risks associated with AR in surgery. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions and set realistic expectations.
Tip 3: Seek Proper Training
If you are a medical professional interested in incorporating AR into your practice, seek proper training and education. Familiarize yourself with the specific tools and software used in AR-assisted surgeries. This will ensure you can effectively and safely utilize this technology.
Tip 4: Collaborate with Experts
Collaboration is key when it comes to implementing AR in surgical procedures. Engage with experts in the field, including surgeons, technologists, and researchers. By working together, you can exchange knowledge, share experiences, and collectively push the boundaries of AR in surgery.
Tip 5: Embrace Continuous Learning
AR technology is evolving rapidly, so it is crucial to embrace continuous learning. Stay updated on new techniques, software updates, and best practices. Attend workshops, webinars, and training sessions to enhance your skills and stay at the forefront of this exciting field.
Tip 6: Evaluate Patient Suitability
Not all patients may be suitable candidates for AR-assisted surgeries. Evaluate each patient’s individual case and consider factors such as their medical history, condition, and potential benefits of using AR. Consult with your colleagues and involve the patient in the decision-making process.
Tip 7: Maintain Ethical Considerations
As with any technological advancement, it is important to maintain ethical considerations. Ensure patient privacy and confidentiality when using AR tools. Adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations set by medical boards and institutions to protect patient rights and well-being.
Tip 8: Foster a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment within your surgical team is crucial for successful integration of AR technology. Encourage open communication, provide training opportunities, and address any concerns or challenges that may arise. By fostering a supportive culture, you can maximize the benefits of AR in abdominal procedures.
Tip 9: Consider Cost and Accessibility
While AR technology holds tremendous potential, it is essential to consider the cost and accessibility factors. Evaluate the financial implications of implementing AR tools and ensure they are accessible to a wide range of healthcare facilities and patients. Advocate for affordable and inclusive use of AR in surgery.
Tip 10: Share Knowledge and Experience
Lastly, share your knowledge and experience with others. Whether through academic publications, presentations, or online platforms, contribute to the collective understanding of AR in surgery. By sharing your insights, you can inspire others and contribute to the advancement of this transformative technology.
In conclusion, the future of surgery is being revolutionized by augmented reality technology, particularly in the field of abdominal procedures. This groundbreaking technology has the potential to greatly enhance surgical precision, improve patient outcomes, and advance medical training. By providing surgeons with real-time, three-dimensional visualizations of the patient’s anatomy, augmented reality allows for more accurate and efficient surgical interventions.
Furthermore, the integration of augmented reality into surgical procedures has the potential to reduce the risk of complications and shorten recovery times for patients. With the ability to overlay vital information, such as CT scans or ultrasound images, directly onto the patient’s body, surgeons can navigate complex anatomical structures with greater ease and accuracy. This not only improves the surgeon’s ability to locate and repair damaged tissues but also minimizes the risk of unintentional damage to surrounding organs.
While augmented reality technology in surgery is still in its early stages, the advancements made so far are promising. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in the field of surgery, further enhancing the capabilities of surgeons and improving patient care. The future of surgery is indeed being transformed by augmented reality, and its impact on abdominal procedures is just the beginning of a new era in surgical innovation.